What Is a Bull Put Spread?
A Bull Put Spread is a credit spread strategy. You sell one put and buy another put with a lower strike:
- Sell 1 Put Option (Higher Strike)
- Buy 1 Put Option (Lower Strike)
Both with same expiry
You receive a net credit upfront. The goal is for the stock to stay above the higher strike, so both options expire worthless and you keep the credit.
When it comes to options trading, understanding the greeks – Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho is critical for building effective strategies. So do check them out, also if you are beginner in options trading I would request you to first have Basic understanding of options ,Option moneyness , How to read option chain table.
Why Use Bull Put Spread Strategy?
-
You’re bullish or expect the stock to stay above a level
-
You want to generate income (from option selling)
-
You want to limit your downside (unlike naked put selling)
-
Works well in rangebound to slightly bullish markets
Bull Put Spread Strategy Example:
Let’s assume:
Detail |
Value |
|---|---|
Current Reliance Price |
₹2,940 |
Sell 1 Put @ ₹2,920 |
Premium ₹50 |
Buy 1 Put @ ₹2,880 |
Premium ₹30 |
Lot Size |
250 shares |
Net Credit Received:
-
Received ₹50 – Paid ₹30 = ₹20
-
Total credit = ₹20 × 250 = ₹5,000
This is your maximum profit potential.
Max Profit & Max Loss:
Scenario |
Calculation |
Amount |
|---|---|---|
Max Profit (RELIANCE > ₹2920) |
Net premium received |
₹5,000 |
Max Loss (RELIANCE < ₹2880) |
Spread – Net premium = ₹40 – ₹20 |
₹20 × 250 = ₹5,000 |
Breakeven Point |
₹2920 – ₹20 = ₹2,900 |
— |
So your risk-to-reward is 1:1, and probability of profit is high if market stays sideways or goes up slightly.
Option Greeks (Basic View)
| Greek | Behavior |
|---|
| Delta | Positive overall (bullish) |
| Theta | Positive — time decay helps you |
| Vega | Slightly negative (IV fall helps) |
| Gamma | Low (stable profit/loss zones) |
Great for weekly selling when IV is high & expiry is close.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Variations:
Weekly Version:
-
Choose near-expiry Puts with tight strikes (e.g., ₹2,940 & ₹2,900)
-
Maximize Theta decay
-
Ideal when Reliance is consolidating
Conservative vs Aggressive:
| Style | Setup Example | Risk | Reward |
|---|
| Conservative | 2920–2880 spread (₹40 gap) | Lower | Lower |
| Aggressive | 2920–2900 spread (₹20 gap) | Higher | Higher |
Payoff Graph – Bull Put Spread (Reliance Example)
Here’s Bull Put Spread payoff graph:
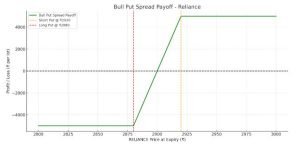
Key Takeaways from the Graph:
-
Flat green zone above ₹2920 → Max profit: ₹5,000
-
Break-even at ₹2900
-
Max loss of ₹5,000 below ₹2880
-
Smooth transition between ₹2920 and ₹2880
This visual helps you see how much you stand to gain or lose depending on where Reliance closes at expiry.
Summary Table: Bull Put Spread (Reliance)
Criteria |
Value |
|---|---|
Strategy Type |
Bullish (Credit Spread) |
Max Profit |
₹5,000 |
Max Loss |
₹5,000 |
Breakeven |
₹2,900 |
Theta Decay Benefit |
Yes |
Vega Sensitivity |
IV drop helps you |
Best Market Condition |
Flat to slightly bullish |
Option Greeks Impact (Explained Simply)
Greek |
Effect in Bull Put Spread |
What It Means Practically |
|---|---|---|
Delta |
Small positive (bullish) |
You’re slightly bullish; upside benefits you |
Theta |
Positive |
Time decay works in your favor — ideal for weekly trades |
Vega |
Negative |
You benefit if implied volatility drops |
Gamma |
Low |
Position behaves stably, not too sensitive to price jumps |
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Adjustments in Bull Put Spread:
1. Stock falls below breakeven (₹2900)
Situation: Reliance is falling and may go below ₹2900
Goal: Reduce or manage loss
Options:
Adjustment Strategy |
What You Do |
Effect |
|---|---|---|
Roll Down & Out |
Shift both puts to lower strikes, further expiry |
Collect more credit, extend time |
Convert to Iron Condor |
Add Bear Call Spread above |
Caps loss, reduces margin |
Buy additional Put |
Add a new lower put (protective) |
Hedge downside if fall looks sharp |
2. Stock rises quickly and trade is already profitable
Situation: Reliance jumps to ₹2960+ within 2-3 days
Goal: Lock in profits early
Options:
Adjustment |
What You Do |
Effect |
|---|---|---|
Exit Entire Spread |
Book profit early |
Avoid theta/gamma risk near expiry |
Roll up puts |
Create a new bull put at higher strikes |
Continue collecting premium if bullish bias remains |
Weekly Options Use Case:
Bull Put Spread works very well with weekly expiries:
-
Sell ATM or slightly OTM put (1 strike below CMP)
-
Buy further OTM put (3–4 strikes lower)
-
Choose high IV weeks (events, results, Fed, RBI etc.)
-
Exit when 60–80% profit is achieved — don’t wait till expiry
Example (Weekly Trade on NIFTY):
-
Nifty @ 22,400
-
Sell 22,350 PE @ ₹40
-
Buy 22,250 PE @ ₹20
-
Net credit = ₹20 × 50 = ₹1,000 per lot
-
Max Loss = ₹5,000
-
Risk:Reward = 1:1, Probability of Profit (POP) ~ 60%
Option Chain Insights:
When scanning for good Bull Put spreads:
-
Check PCR (Put Call Ratio) near strike → >1 is bullish
-
IV rank should be high
-
Use OI buildup to pick strike where support exists
-
Avoid low volume or wide bid-ask spread strikes
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
When NOT to Use a Bull Put Spread (And Why)?
The Bull Put Spread is a credit spread used when you’re moderately bullish, but there are times when this strategy can backfire or underperform. Here’s when to avoid it:
1. When Market Trend Is Uncertain or Choppy
-
Why: If the market is ranging or volatile without direction, your short put strike may get tested.
-
Risk: You may face quick drawdowns due to sharp intraday swings.
-
Better Option: Wait for confirmation of support or use wider spreads.
2. When You’re Very Bullish
-
Why: The Bull Put Spread has limited reward, so if you expect a sharp rally, this won’t capture much of the move.
-
Better Option: Consider a bull call spread or naked puts (if comfortable with higher margin/risk).
3. During High IV Events
-
Why: Though you receive more premium, high IV before events like RBI policy, earnings, or budget can lead to IV crush and erratic moves.
-
Risk: Sharp moves or whipsaws post-event can break support levels.
-
Better Option: Wait post-event, when direction is clearer.
4.Too Close to Expiry With Price Near Short Strike
-
Why: With 2–3 days to expiry and price hovering near your short put, gamma risk increases. Small price changes can move the P&L dramatically.
-
Risk: You may be forced to adjust or exit at a loss.
-
Better Option: Roll the spread to next expiry earlier or reduce position size.
5. When Strike Selection Is Too Aggressive
-
Why: Choosing short puts too close to current price increases your chance of being breached.
-
Risk: The trade becomes too directional, defeating the purpose of a credit spread.
-
Better Option: Choose strikes with better support (technical + option OI) and use proper risk-reward filters.
6. When Margin Requirements Are High
-
Why: Sometimes margin for Bull Put Spreads (especially far OTM) may be inefficient relative to the small credit received.
-
Risk: Capital inefficiency, poor returns on risk.
-
Better Option: Use more capital-efficient setups or increase lot size with wide spreads.
Pro Tip: Always ensure you have a clear bullish bias with support confirmation and that IV is not expected to expand sharply during your trade duration.
The Bull Put Spread is great for “stay above this level” scenarios with support zones, but avoid it if there’s volatility uncertainty, event risk, or lack of directional clarity.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Tips & Tricks for Bull Put Spread:
Strike Selection
-
Use technical support zones + open interest build-up for your short put strike.
-
Keep at least 2–4% buffer below CMP for safety.
-
Wider spreads (e.g., 100-point on Nifty) reduce risk but also reduce credit.
Time to Expiry
-
Ideal duration: 7 to 20 days.
-
Avoid last 2–3 days unless you’re adjusting or closing positions.
-
Weekly expiries offer faster time decay but require faster decision-making.
Volatility Edge
-
Enter when IV is high and expected to drop (post-event, before long weekends).
-
Avoid initiating during low IV, as expansion can hurt your mark-to-market.
Greeks to Watch
-
Delta: Combined delta of spread should be positive (~+15 to +30).
-
Theta: Positive — time decay works in your favor.
-
Vega: Slightly negative — strategy benefits from falling IV.
-
Gamma: Low, but spikes near expiry — avoid risky moves late in the week.
Adjustments (if trade goes wrong)
-
Roll down or out (shift to next expiry).
-
Add another spread at lower strikes to manage delta.
-
Close the position early if price breaks below short put strike with volume.
Best Use Cases
-
Nifty/BankNifty post-correction setups
-
Stocks showing base formation or breakout retests
-
Stable weeks with no major events or macro risk
Conclusion: Bull Put Spread Strategy
The Bull Put Spread is one of the most popular and reliable options strategies for traders with a moderately bullish outlook.
It offers the dual advantage of earning a net credit (premium income) while keeping the risk limited and defined. This makes it especially useful for traders who want to avoid the high costs and unlimited risk associated with naked option writing.
By choosing strike prices wisely — typically below key support levels or high OI zones — this strategy can help you profit even when the underlying stock/index doesn’t move much, as long as it stays above the breakeven point by expiry.
The Bull Put Spread is a probability-focused income strategy. It rewards patience, proper strike selection, and volatility timing. Use it when you expect stability or slow upward movement — and avoid it during chaotic or uncertain market conditions.
Learn Covered Call Option Strategy here
Learn Bull Call Spread Strategy here
Disclaimer:
This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. Trading in derivatives like options involves substantial risk and is not suitable for all investors.
All examples, strategies, and calculations (including those involving NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, or any other instruments) are hypothetical and meant solely to illustrate how options strategies work under certain conditions.
Market conditions, pricing, and premiums may vary significantly in real-time trading. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
You are advised to consult with a SEBI-registered investment advisor or a qualified professional before making any investment or trading decisions. Always perform your own due diligence.
The author or platform is not responsible for any direct or indirect loss arising from any information provided here.




