The Strangle Strategy is a powerful tool for traders who expect a big move in the market but want to reduce the cost compared to a Straddle. It’s a favorite for event-based trading on stocks and indices like Nifty or Bank Nifty.
When it comes to options trading, understanding the greeks – Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho is critical for building effective strategies. So do check them out, also if you are beginner in options trading I would request you to first have Basic understanding of options ,Option moneyness , How to read option chain table.
Let’s dive deep and understand Strangle strategy in the simplest way possible. We will learn both long and short strangle strategy step by step.
What is a Strangle Strategy?
A Long Strangle involves:
-
Buying 1 OTM Call
-
Buying 1 OTM Put
Both with the same expiry date but different strike prices.
Market Outlook
You expect a big movement in either direction (but don’t know which way).
Types of Strangle Strategies
Type |
Components |
Market View |
Risk |
Reward |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Long Strangle |
Buy 1 OTM Call + Buy 1 OTM Put |
Expecting high volatility |
Limited |
Unlimited |
Short Strangle |
Sell 1 OTM Call + Sell 1 OTM Put |
Expecting low volatility |
Unlimited |
Limited |
We will understand the short strangle strategy later in the post, first will focus on long strangle strategy.
Long Strangle Strategy Example (Nifty)
-
Underlying: Nifty trading at ₹22,000
-
Buy 1 OTM Call at ₹22,200 – Premium = ₹90
-
Buy 1 OTM Put at ₹21,800 – Premium = ₹100
Total Premium Paid = ₹190 × 50 (lot size) = ₹9,500
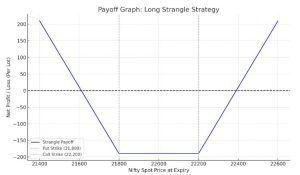
Long Strangle Strategy Payoff Graph
Here’s the payoff graph for the Long Strangle Strategy, based on the Nifty example:
-
Breakeven points: ₹21,610 and ₹22,390
-
Maximum loss: Limited to the ₹190 premium paid per unit
-
Profit potential: Unlimited if Nifty moves significantly above or below the strike range
Long Strangle Strategy Payoff Graph Summary
Nifty at Expiry |
Net Profit / Loss |
|---|---|
₹22,000 |
-₹9,500 (Max loss) |
Above ₹22,390 |
Profit starts |
Below ₹21,610 |
Profit starts |
Move > ₹390 |
Unlimited profit |
Max Loss: ₹9,500
Breakeven Points: ₹21,610 and ₹22,390
Max Profit: Unlimited
Impact of Option Greeks on Long Strangle Strategy
Delta (Δ) – Sensitivity to Price Movement
-
Call has positive Delta; Put has negative Delta.
-
Net Delta is close to zero at entry.
-
As the market moves up/down significantly, one leg gains delta fast, boosting profits.
Good for: Sharp price movement in either direction.
Neutral markets = no delta advantage.
Gamma (Γ) – Acceleration of Delta
-
Gamma is moderate (less than a Straddle, more than deep OTM).
-
As price moves closer to one of the strikes, Gamma helps the winning leg gain rapidly.
Favorable when the market makes a fast move.
Low gamma effect if price stagnates.
Theta (Θ) – Time Decay
-
Strangle is a net debit strategy, so Theta is negative.
-
You lose money daily if the underlying remains in the range.
-
Time decay accelerates near expiry, especially if price is near midpoint.
Can be minimized by entering earlier or exiting before expiry.
Major risk if market doesn’t move.
Vega (ν) – Implied Volatility Impact
-
Strangle has positive Vega.
-
Rising IV boosts both option premiums — even without price movement.
Enter before a major event when IV is low
Avoid entry when IV is already high
Rho (ρ) – Interest Rate Sensitivity
Negligible effect for short-term Indian options.
Greeks Summary – Long Strangle
Greek |
Impact on Strangle |
Description |
|---|---|---|
Delta |
Neutral at start |
Becomes directional as price moves |
Gamma |
Moderate |
Helps rapid P/L acceleration near strikes |
Theta |
Negative |
Loses value if price stagnates |
Vega |
Positive |
Gains from rising IV |
Rho |
Minimal |
Ignored for short expiries |
If you’re looking for a broker that offers speed, transparency, and advanced tools, Dhan is one of the best choices today. With zero brokerage on delivery trades and intuitive charts, Dhan is built for both beginners and pro traders. Invest in Stocks, F&O, Commodities, Currency, ETFs, Mutual Funds, SGBs, IPOs, SIPs and much more.
Click Here to Open Your Free Dhan Account
No paperwork. No account opening charges. Get started in 5 minutes! Dhan also offers advanced tools like TradingView & Options Trader built-in.
When to Use a Long Strangle?
Use a Long Strangle when:
-
Expecting big movement but want a cheaper trade than a Straddle.
-
Before events like:
-
RBI interest rate decision
-
Union Budget
-
Company earnings
-
Election results
-
-
IV is moderate or low, with potential to rise
When NOT to Use a Long Strangle?
Avoid a long Strangle when:
-
Market is range-bound and expected to stay quiet
-
Implied Volatility is already high
-
You’re close to expiry and price hasn’t moved
Tips & Tricks for Beginners
Choose strikes with good liquidity (high open interest)
Don’t enter too close to expiry unless you’re expecting a breakout
Monitor India VIX: Lower VIX = better time to enter
Exit before event result if IV rises — you’ll profit even without movement
Use tools like Dhan customized option strategy builder to analyse greeks
Comparison: Strangle vs Straddle
| Feature | Straddle | Strangle |
|---|
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Breakeven Range | Narrow | Wider |
| Profit Potential | Unlimited | Unlimited |
| Theta Risk | Higher | Slightly lower |
| Best For | Strong IV events | Cost-effective moves |
Let us know understand the short strangle strategy in the similar way.
What is a Short Strangle?
A Short Strangle Strategy is an income-generating, non-directional strategy where a trader:
-
Sells 1 Out-of-the-Money (OTM) Call
-
Sells 1 Out-of-the-Money (OTM) Put
-
Same expiry date, different strikes
Market View:
You expect the market to stay within a range (low volatility).
Short Strangle Example (Nifty)
-
Underlying: Nifty at ₹22,000
-
Sell 1 OTM Call at ₹22,200 – Premium = ₹90
-
Sell 1 OTM Put at ₹21,800 – Premium = ₹100
Total Premium Collected = ₹190 × 50 (lot size) = ₹9,500
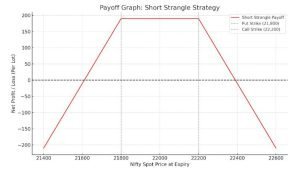
Short Strangle Strategy Payoff Graph
Here’s the payoff graph for the Short Strangle Strategy:
-
Max Profit: ₹190 (total premium received)
-
Breakeven Points: ₹21,610 and ₹22,390
-
Unlimited Loss: If Nifty moves sharply below or above the breakevens
This strategy is suitable for range-bound markets but carries high risk if volatility spikes.
Payoff Summary – Short Strangle
Nifty at Expiry |
Net Profit / Loss |
|---|---|
₹22,000 |
+₹9,500 (Max profit) |
Above ₹22,390 |
Loss begins |
Below ₹21,610 |
Loss begins |
Sharp move ↑↓ |
Unlimited loss |
Max Profit: ₹9,500
Max Loss: Unlimited if price moves significantly
Breakeven Points: ₹21,610 and ₹22,390
Impact of Option Greeks on Short Strangle Strategy
Delta (Δ) – Price Sensitivity
-
Call has negative Delta, Put has positive Delta
-
Net Delta is close to 0 at entry
-
If market moves, Delta shifts against you (losses build quickly)
Gamma (Γ) – Rate of Delta Change
-
Short Strangles have negative Gamma
-
If price moves away from strike, delta changes rapidly → positions lose faster
Theta (Θ) – Time Decay
- Positive Theta
- Time decay benefits the seller daily
- Faster decay near expiry
Vega (ν) – Volatility Sensitivity
- Negative Vega
- Rising volatility hurts the seller
- Enter when IV is high and expected to fall
Rho (ρ) – Interest Rate Sensitivity
Minimal impact for short-dated options
Greeks Summary – Short Strangle
| Greek | Impact | Description |
|---|
| Delta | Neutral at start | Turns directional if price moves |
| Gamma | Negative | Hurts if market trends strongly |
| Theta | Positive | Time decay benefits seller |
| Vega | Negative | Rising IV leads to premium expansion |
| Rho | Minimal | Not significant for near-term trades |
When to Use a Short Strangle?
Use this strategy when:
-
You expect sideways movement or consolidation
-
Implied Volatility (IV) is high
-
You’re comfortable taking defined risk measures (like stop-loss or hedge)
Good for:
-
Expiry week range-bound markets
-
News/event after IV spike
When NOT to Use a Short Strangle?
Avoid this strategy when:
-
You expect a big directional move (up or down)
-
IV is very low (no room for premium compression)
-
You cannot monitor the trade (due to unlimited risk)
Pro Tips for Short Strangle Traders
Use stop-losses or hedges to manage unlimited risk
Watch India VIX: Enter when VIX is high
Enter early in the week to benefit from Theta
Place strikes far OTM to increase safety range
Use tools like Dhan customized option strategy builder to manage risk.
Short Strangle vs Long Strangle
Feature |
Long Strangle |
Short Strangle |
|---|---|---|
Directional Bias |
Expect big move |
Expect no big move |
Premium |
You pay premium |
You collect premium |
Risk |
Limited to premium paid |
Unlimited |
Reward |
Unlimited |
Limited to premium received |
Time Decay (Theta) |
Negative |
Positive |
IV Sensitivity |
Positive (needs IV rise) |
Negative (benefits from IV drop) |
Short Strangle vs Long Strangle Payoff Graph
Here is the visual comparison between the Long Strangle (green) and Short Strangle (red) strategies:

-
The Long Strangle profits with big moves (up or down) beyond breakeven points.
-
The Short Strangle profits only if the market remains range-bound, but carries unlimited loss risk if the market breaks out.
If you’re looking for a broker that offers speed, transparency, and advanced tools, Dhan is one of the best choices today. With zero brokerage on delivery trades and intuitive charts, Dhan is built for both beginners and pro traders. Invest in Stocks, F&O, Commodities, Currency, ETFs, Mutual Funds, SGBs, IPOs, SIPs and much more.
Click Here to Open Your Free Dhan Account
No paperwork. No account opening charges. Get started in 5 minutes! Dhan also offers advanced tools like TradingView & Options Trader built-in.
Final Thoughts
The Strangle Strategy is a flexible and cost-effective way to trade volatility in the Indian options market. With limited risk and unlimited profit potential, it’s perfect when you’re expecting a big move, but don’t want to pay the high premium of a Straddle.
Manage your Greeks well especially Theta and Vega and always plan your exit before the market moves against you.
Learn Call Butterfly Spread Strategy here
Learn Bear Call Ladder Strategy here
Learn Bull Put Spread Strategy here
Learn Covered Call Option Strategy here
Learn Bull Call Spread Strategy here
Learn Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy here
Disclaimer:
This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. Trading in derivatives like options involves substantial risk and is not suitable for all investors.
All examples, strategies, and calculations (including those involving NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, or any other instruments) are hypothetical and meant solely to illustrate how options strategies work under certain conditions.
Market conditions, pricing, and premiums may vary significantly in real-time trading. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
You are advised to consult with a SEBI-registered investment advisor or a qualified professional before making any investment or trading decisions. Always perform your own due diligence.
The author or platform is not responsible for any direct or indirect loss arising from any information provided here.




