If you’re looking for an options trading strategy that allows you to profit in a range-bound market, the Call Butterfly Spread might be the perfect fit. Call Butterfly Spread Strategy is cost-effective, has limited risk, and offers a clearly defined risk-to-reward ratio.
When it comes to options trading, understanding the greeks – Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho is critical for building effective strategies. So do check them out, also if you are beginner in options trading I would request you to first have Basic understanding of options ,Option moneyness , How to read option chain table.
Let’s dive deep and understand call butterfly spread strategy in the simplest way possible.
What is a Call Butterfly Spread?
The Call Butterfly Spread is a neutral options strategy created by combining bull call spread and bear call spread. It is designed to profit when the underlying stock/index remains close to a specific price at expiry.
Key Characteristics:
-
Market Outlook: Neutral
-
Cost: Low to moderate
-
Risk: Limited
-
Reward: Limited
-
Complexity: Moderate
Structure of the Strategy:
The Call Butterfly Spread consists of three different strike prices with the same expiry date:
-
Buy 1 ATM Call Option (Lower strike)
-
Sell 2 OTM Call Options (Middle strike)
-
Buy 1 Further OTM Call Option (Higher strike)
All options are of the same underlying asset and expiry.
Call Butterfly Spread Example (Nifty 50)
Let’s say Nifty is currently trading at ₹22,000.
Here’s how a Call Butterfly Spread can be constructed:
Action |
Option Type |
Strike Price |
Premium (Approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
Buy |
Call |
₹21,800 |
₹250 |
Sell (x2) |
Call |
₹22,000 |
₹150 × 2 = ₹300 |
Buy |
Call |
₹22,200 |
₹100 |
Net Premium Paid:
-
Paid: ₹250 (Buy) + ₹100 (Buy) = ₹350
-
Received: ₹300 (Sell)
-
Net Cost = ₹350 – ₹300 = ₹50 per lot
Lot size of Nifty = 50
Total Investment = ₹50 × 50 = ₹2,500
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Call Butterfly Spread Payoff Graph Explained
Here’s what the Call Butterfly Spread Payoff Graph looks like:
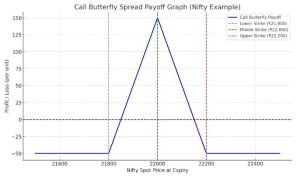
Here is the Call Butterfly Spread Payoff Graph based on the Nifty example:
- Maximum Profit occurs when Nifty closes at ₹22,000.
- Maximum Loss is limited to the premium paid (₹2,500).
- Breakeven Points: Around ₹21,850 and ₹22,150.
Payoff Summary Table (Based on Nifty Call Butterfly Spread)
| Nifty at Expiry | Profit / Loss (Approx.) |
|---|
| ₹21,800 | -₹2,500 (Max Loss) |
| ₹22,000 | +₹2,500 (Max Profit) |
| ₹22,200 | -₹2,500 (Max Loss) |
| ₹21,850 or ₹22,150 | ₹0 (Break-even) |
When to Use Call Butterfly Spread Strategy?
Use this strategy when you expect:
-
The underlying stock or index to stay within a range.
-
Low volatility in the market.
-
A major event is over and prices are expected to consolidate.
Ideal Scenario:
You believe Nifty will remain around ₹22,000 till expiry — not go much higher or lower.
When NOT to Use Call Butterfly Spread Strategy?
Avoid this strategy when:
-
The market is highly volatile.
-
Big news or events are approaching (e.g. RBI announcements, elections).
-
You’re unsure about the direction of the market.
Tips & Tricks for Call Butterfly Spread Strategy
-
Always check Implied Volatility (IV): Avoid during high IV spikes; premiums become expensive.
-
Choose strikes wisely: Select strike prices close to current market price.
-
Stick to liquid contracts: Use Nifty or Bank Nifty; stock options may lack liquidity.
-
Avoid holding till expiry: Exit before expiry if you’re in profit.
-
Use Greek analysis: Focus on Theta (time decay) – it works in your favor.
-
Paper trade first: Practice this strategy in a demo account before risking real money.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Pros and Cons Call Butterfly Spread Strategy
Advantages:
-
Low cost
-
Limited risk and reward
-
Works well in stagnant markets
-
Defined profit/loss zone
Disadvantages:
-
Limited profit
-
No use in trending markets
-
Complicated for absolute beginners
Impact of Option Greeks on Call Butterfly Spread
Understanding how Option Greeks impact a Call Butterfly Spread is crucial to managing risk and timing your entries and exits effectively.
Strategy Recap:
In a Call Butterfly Spread, you:
-
Buy 1 ITM Call
-
Sell 2 ATM Calls
-
Buy 1 OTM Call
All with the same expiry.
This creates a limited risk, limited reward strategy optimized for range-bound markets.
1.Delta (Δ): Directional Bias
-
A properly structured Butterfly Spread has a net Delta close to zero at initiation.
-
As the underlying price moves towards the middle strike, the net Delta becomes more neutral to slightly positive, increasing your potential profit.
-
If price moves too far outside the wings, Delta becomes less favorable.
Benefit: Delta stays balanced unless the market breaks out.
Risk: If the market trends strongly, you miss out.
2.Gamma (Γ): Change in Delta
-
Gamma is highest near the middle strike price.
-
As expiry approaches and the underlying nears the middle (ATM) strike, Gamma increases sharply.
-
This causes profits to spike rapidly near expiry only if the price settles within the profit zone.
Benefit: You get a sudden rise in gains if the price moves into your profit zone near expiry.
Risk: Outside the range, Gamma helps little, and you can’t recover the premium paid.
3.Theta (Θ): Time Decay
-
Theta works in your favor as you are net selling premium (via 2 ATM calls).
-
This makes Butterfly spreads a time-positive strategy — you benefit from time decay as long as the market stays within range.
-
Closer to expiry, theta decay accelerates and works to your advantage only if the price is near the middle strike.
Benefit: Time decay helps you when price stays within the range.
Risk: If market moves outside your breakevens, theta alone won’t save you.
4.Vega (ν): Volatility Sensitivity
-
Vega is slightly negative in a Call Butterfly because you’re selling more options than buying.
-
This means you benefit when implied volatility (IV) falls after you enter the trade.
-
An IV crush (drop in volatility) makes this strategy more profitable quickly.
Benefit: Enter when IV is high; exit when it drops.
Risk: If IV rises after entry, your position may show a loss even if price stays in range.
5.Rho (ρ): Interest Rate Sensitivity
-
Minimal impact, especially on near-term expiries in the Indian market.
-
Typically ignored by retail traders unless dealing in long-dated options.
Greeks Summary Table – Call Butterfly Spread
Greek |
Effect on Strategy |
What It Means |
|---|---|---|
Delta |
Near neutral initially |
Balanced position, low directional bias |
Gamma |
High near middle strike |
Sharp P/L swings near expiry if in range |
Theta |
Positive |
Benefits from time decay in range-bound |
Vega |
Slightly negative |
Prefers falling IV (after entry) |
Rho |
Negligible |
Minimal impact in short-term positions |
Final Tips Based on Greeks
- Enter when IV is high, so falling IV adds to profits.
- Hold closer to expiry only if price is near middle strike to benefit from Gamma and Theta.
- Don’t chase trending markets — Delta won’t help you much outside your breakeven range.
- Use risk-to-reward tools like Dhan customized option strategy builder
Conclusion: Is Call Butterfly Spread Right for You?
The Call Butterfly Spread Strategy is ideal for experienced beginners who want to try non-directional strategies with defined risk and limited capital. It’s especially useful in sideways or consolidating markets like after major earnings or budget announcements.
Whether you’re trading Nifty, Bank Nifty, or highly liquid stock options, this strategy offers a low-risk, medium-reward setup perfect for ranging market conditions.
Learn Bear Call Ladder Strategy here
Learn Bull Put Spread Strategy here
Learn Covered Call Option Strategy here
Learn Bull Call Spread Strategy here
Learn Call Ratio Back Spread Strategy here
Disclaimer:
This content is for educational purposes only and does not constitute financial or investment advice. Trading in derivatives like options involves substantial risk and is not suitable for all investors.
All examples, strategies, and calculations (including those involving NIFTY, BANKNIFTY, or any other instruments) are hypothetical and meant solely to illustrate how options strategies work under certain conditions.
Market conditions, pricing, and premiums may vary significantly in real-time trading. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
You are advised to consult with a SEBI-registered investment advisor or a qualified professional before making any investment or trading decisions. Always perform your own due diligence.
The author or platform is not responsible for any direct or indirect loss arising from any information provided here.




