In options trading, Vega is one of the five key Greeks that help traders measure risk and forecast option price movements. Learning how to use Vega in options trading will definitely gives you an edge over normal traders.
Vega is a powerful tool in the options trader’s arsenal. Whether you trade Nifty, Bank Nifty, or FinNifty, understanding Vega helps you:
-
Navigate volatile news weeks
-
Time your option buying/selling better
-
Avoid IV (Implied Volatility) crush post-events
-
Hedge smarter using Greeks
India’s options market is driven heavily by Nifty, Bank Nifty, and FinNifty. Since these indices can experience sudden volatility (due to RBI events, elections, global cues), understanding Vega is vital.
Event-based trades (e.g., RBI announcements) usually cause a spike in IV, making options more expensive.
Traders use Vega to profit from these volatility spikes by buying options before IV increases.
When it comes to options trading, understanding the greeks – Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, and Rho is critical for building effective strategies.
This article provides a deep dive into Vega, its relationship with Delta, Gamma, Theta and its practical applications, and examples to illustrate its significance.
Before we go in depth in Vega I would request you to have Basic understanding of options ,Option moneyness , How to read option chain table.
By understanding these Options Greeks traders can make more informed decisions about buying, selling or holding options positions.
There are majorly four Greeks one should be aware i.e. Delta, Gamma, Vega, Theta.
- Delta – Delta is the amount an option price (premium) is expected to move based on a 1 rupee change (up or down) in the underlying stock or index.
- Gamma – It helps in measuring Rate of change of delta.
- Vega – This calculate rate of change of premium depending up on change in volatility.
- Theta – It helps in knowing the effect on premium in respect to days or time left for expiry
As of now let us concentrate on Vega in options trading.
but before moving straight to Vega just a brief reminder about delta gamma and Theta is necessary so that you can connect the dots.
“Delta is the amount an option price (premium) is expected to move based on a 1 rupee change in the underlying stock”.
In other words Delta of an option helps in Measuring how an options value changes with respect to the change in the underlying.
Most of the beginners in option trading assume that when a stock moves Rs.1, the price of options premium based on that stock will move more than Rs.1.
Always remember the option is a derivative contract, it derives its value from its respective underlying, it can never move faster than the underlying. In reality it does not work like this at all.
This is when we need to be aware of Delta of an option. By knowing this you will be able to find ” how many points will the option premium change for every 1 point change in the underlying.
Whereas Gamma measures the rate of change of Delta for every 1 point change in the price of the underlying asset. In other words Gamma of an option helps us to find the corresponding change in the delta of the option with respect to the change in the underlying value.
Delta measures how much an option’s price will change for a 1 point move in the underlying asset. Gamma explains how that Delta itself will change if the underlying asset continues to move.
Gamma peaks when the option is at-the-money (ATM). This is because small changes in the underlying price can quickly alter the probability of the option expiring in the money (ITM) or out of the money (OTM).
For deeply ITM or OTM options, the Delta is less sensitive to underlying price changes, resulting in a smaller Gamma. As options approach expiration, Gamma increases for ATM options. This phenomenon, often called Gamma risk, makes it challenging to manage positions near expiry.
Gamma is positive for both call and put options. It ensures that Delta moves predictably in response to changes in the underlying, regardless of the option type.
Talking about Theta, it is a critical component of options trading and refers to the time decay of an option. Theta measures how much an option’s price decreases as time passes, assuming all other factors remain constant.
Theta in options trading is critical because it directly impacts the profitability of your trades, especially in terms of how time affects the value of your options.
- For Option Buyers: Knowing Theta helps you avoid holding options for too long in stagnant markets.
- For Option Sellers: It helps you profit from the predictable erosion of time value.
- For All Traders: Theta is a core component of options pricing and directly affects your risk/reward.
Without a strong understanding of Theta, you could lose money simply because “time is money” in options trading.
Theta measures the rate at which the time value of an option decreases as it approaches its expiry date.
Theta is generally negative for option buyers and positive for option sellers.
Theta is expressed as the amount the option price will lose per day due to time decay.
Remember you do not need to calculate these option greeks values manually as it is available with many brokers in built in their trading platform.
and if you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
now let us comeback to the original topic Vega and how it will help you to be a better option trader.
What is Vega in Options Trading?
Vega measures an option’s sensitivity to changes in implied volatility (IV). It tells traders how much an option’s premium will change if IV increases or decreases by 1 percentage point.
Key Points About Vega
-
Higher Vega = Higher impact of IV on option prices.
-
Vega is highest for ATM options and decreases as options go ITM or OTM.
-
Longer-term options have higher Vega than short-term options.
Example:
Suppose you buy a Nifty 50 ATM Call Option priced at ₹200 with a Vega of 0.10. If IV increases by 1%, the option’s price will increase by ₹10 to ₹210.
Vega’s Relationship with Other Greeks:
Greek |
Linked Behavior with Vega |
|---|---|
Delta |
Delta options with values close to 0.5 = higher Vega |
Gamma |
Vega is high when Gamma is high (ATM options) |
Theta |
Higher Vega often means more Theta (time decay) |
Rho |
Vega is mostly independent of Rho |
What is Implied Volatility (IV)?
Implied Volatility (IV) represents the market’s expectation of future price fluctuations of an underlying asset. Unlike historical volatility, which looks at past movements, IV is forward-looking and derived from current option prices.
In simple terms, implied volatility(IV) is the opinion of the market on the stock or index next potential move. If the implied volatility is high, the market thinks the security has potential for large price swings in both(up/down) direction.
Where as low IV implies the stock will not move as much upon option expiration. It tells us about what the market thinks on the price movement of the underlying. Implied volatility does not provide a forecast with respect to market direction.
IV give you a sense for how volatile the market may be in the future, it can also help you determine the likelihood of a stock reaching a specific price by a certain time. That can be crucial information when you’re choosing specific options contracts to trade.
Since most option trading volume usually occurs in at-the-money (ATM) options, these are the contracts generally used to calculate IV.
How Does IV Affect Option Prices?
-
Higher IV – Higher Option Premiums (as uncertainty increases).
-
Lower IV – Lower Option Premiums (as the market expects stability).
Vega’s Dependence on IV
Since Vega measures an option’s sensitivity to IV, a high Vega means the option price will significantly change with IV movements. Traders need to anticipate IV changes before entering trades.
Example: How IV Changes Affect Vega:
Nifty 50 ATM Call Option |
Price |
Vega |
IV Change |
New Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Initial IV: 15% |
₹200 |
0.10 |
+2% |
₹220 |
Initial IV: 15% |
₹200 |
0.10 |
-2% |
₹180 |
Thus, a 2% rise in IV increases the option premium by ₹20, while a 2% drop reduces it by ₹20.
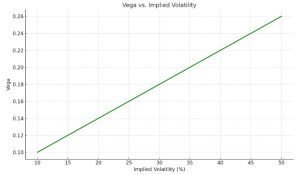
Here’s the graph of Vega vs. Implied Volatility (IV), It demonstrates how Vega increases as IV rises, showing why options become more sensitive in volatile markets.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Vega’s Behavior in Different Market Conditions:
1. High IV vs. Low IV Environments
-
High IV (e.g., before earnings or major events) – Option prices increase, favoring option sellers.
-
Low IV (stable market periods) – Cheaper options, favoring buyers who expect volatility spikes.
2. Vega Over Time to Expiration
-
Long-term options have higher Vega – More time means greater uncertainty.
-
Short-term options have lower Vega – Less time left, so volatility changes have a smaller effect.
Here’s the graph of Vega vs. Days to Expiry, It shows how Vega decreases as the option approaches expiry — a core concept in options trading.

Vega Vs Other Greeks:
1. Vega vs. Delta
-
Delta measures price sensitivity, while Vega measures IV sensitivity.
-
ATM options have high Delta and high Vega, meaning their prices fluctuate due to both market moves and IV shifts.
-
Deep ITM/OTM options have low Vega because IV impacts them less.
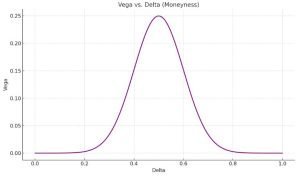
Here’s the graph of Vega vs. Delta. This graph shows that Vega peaks at Delta ≈ 0.5, meaning ATM (At The Money) options are most sensitive to changes in implied volatility.
2. Vega vs. Gamma
-
Gamma measures how Delta changes; Vega influences how the option price reacts to IV changes.
-
High Vega and high Gamma mean extreme price swings in volatile markets.
Here is the graph comparing Vega vs Gamma across different strike prices:
This graph shows:
-
Both Vega and Gamma peak around the ATM (At-the-Money) strike.
-
Gamma is sharper and narrower.
-
Vega has a broader curve, showing it affects a wider range of strikes.

3. Vega vs. Theta
-
Theta measures time decay (how an option loses value over time).
-
High Vega usually means high Theta – Options decay faster when IV is high.
Here is the graph comparing Vega vs Theta across different strike prices:

-
Vega peaks at ATM, representing high sensitivity to volatility.
-
Theta is most negative at ATM, showing the highest time decay.
-
As you move ITM or OTM, both Vega and Theta decrease.
Example: Time Decay & Vega Impact
Option Type |
Theta (Daily Loss) |
Vega |
Expected IV Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
ATM (30 days left) |
₹-2.5 |
High |
Significant |
ATM (5 days left) |
₹-8 |
Low |
Minimal |
Takeaway: Options lose value faster as expiration approaches, reducing Vega’s influence.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Practical Examples of Vega in FnO Trading:
Trading a Nifty 50 ATM Call Option with High Vega
-
Current Nifty 50 Price: 18,000
-
ATM Call Option Price: ₹250
-
Vega: 0.15
-
IV: 18%
Scenario 1: IV Rises to 22%
-
IV change = +4%
-
Price Increase = 0.15 × 4 = ₹60
-
New Option Price: ₹310
Scenario 2: IV Drops to 14%
-
IV change = -4%
-
Price Drop = 0.15 × 4 = ₹60
-
New Option Price: ₹190
Tip: Traders must predict IV changes before buying or selling options!
Vega in NSE Option Chain Analysis
When you open the option chain (e.g., Nifty or Bank Nifty on NSE):
-
Look under “Greeks” if available (some brokers such as Dhan platform show this).
-
Find Vega for different strike prices.
-
Focus on ATM strikes for volatility trades.
Rule of thumb:
Higher Vega = Higher price sensitivity to IV. Use this for IV crush or IV spike plays.
Strategies Leveraging Vega:
1. Long Vega Strategies (When You Expect IV to Rise)
-
Long Straddle → Buy ATM Call + ATM Put
-
Long Strangle → Buy OTM Call + OTM Put
-
Vega Benefits: Profitable if IV rises
2. Short Vega Strategies (When You Expect IV to Fall)
-
Short Straddle → Sell ATM Call + ATM Put
-
Short Strangle → Sell OTM Call + OTM Put
-
Vega Risk: Losses if IV spikes unexpectedly
Common Mistakes Traders Make with Vega
-
Ignoring IV before entering trades – Overpaying for expensive options.
-
Selling options with high Vega before earnings – Risky due to potential IV spike.
-
Not considering Vega’s drop as expiration nears – Leads to miscalculations.
How Vega Behaves Across Different Expirations:
Vega is highest for long-term options and lowest for near-expiry options. This happens because:
-
More time to expiration → Higher Vega (uncertainty increases the impact of volatility).
-
Less time to expiration → Lower Vega (little room for volatility to influence prices).
Example: Bank Nifty Options
-
A 60-day ATM option has a Vega of 0.20.
-
A 10-day ATM option has a Vega of 0.05.
-
If IV increases by 3%:
-
60-day option price rises significantly.
-
10-day option barely moves.
-
Lesson: Long-term traders should focus on high Vega options, while short-term traders should account for Vega decay.
The Relationship Between Vega and Liquidity:
-
Highly liquid options (Nifty 50, Bank Nifty) tend to have lower Vega fluctuations because IV changes less frequently.
-
Illiquid options (mid-cap stocks) can have extreme Vega shifts due to sudden IV spikes.
Example: Comparing Vega of Liquid vs. Illiquid Options
Option Type |
Vega (Low IV) |
Vega (High IV) |
Liquidity Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Nifty 50 ATM Call |
0.12 |
0.15 |
Low fluctuation |
Small-Cap Stock ATM Call |
0.20 |
0.50 |
High fluctuation |
How Vega Changes Around Major Events:
Vega increases before major market events and crashes afterward.
Examples of Events That Impact Vega:
-
Earnings Reports (Reliance, TCS, HDFC Bank) – Vega spikes as traders anticipate volatility.
-
RBI Interest Rate Decisions – Vega rises in Bank Nifty options before announcements.
-
Budget Announcements – Increased Vega in index options due to policy uncertainty.
Example: Vega Before and After RBI Policy Announcement
-
2 days before the announcement:
-
Bank Nifty ATM option premium: ₹300
-
Vega: 0.18
-
IV: 25%
-
-
After the announcement (IV drops to 20%)
-
Vega decreases – Option price falls.
-
New price: ₹250
-
Tip: Avoid buying high Vega options right before major events unless you expect continued IV expansion.
Weekly vs. Monthly Expiry – Vega Differences
Type |
Vega Level |
Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
Weekly |
Lower |
Sellers (Theta plays) |
Monthly |
Higher |
Buyers (Vega plays) |
Event weeks (like RBI or Budget) – Monthly options may have better Vega moves. Avoid buying weekly options during low-IV phases as Vega won’t help much!
Vega and Market Sentiment Analysis
Vega is closely linked to fear and greed in the market.
-
High Vega = Fear or uncertainty.
-
Low Vega = Stability and complacency.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Using the India VIX to Predict Vega Movements
-
India VIX (Volatility Index) measures overall market IV.
-
When India VIX spikes, Vega increases across all options.
-
When India VIX falls, Vega collapses, reducing option premiums.
Example: India VIX and Vega Impact
India VIX Level |
Expected Vega Behavior |
Trading Implication |
|---|---|---|
10-15 (Calm Market) |
Low Vega |
Cheap options, good for buying |
20-30 (Moderate Fear) |
Increasing Vega |
Higher premiums, good for sellers |
40+ (Extreme Panic) |
High Vega |
Expensive options, risky to buy |
Tip: Vega can be used to time entry and exit points based on market fear levels.
India VIX – Where to Track & How to Use?
-
India VIX is the official volatility index in India.
-
It reflects market fear and expectation of movement in Nifty over the next 30 days.
How to use:
-
If India VIX is rising, expect option premiums to rise.
-
High VIX = high Vega sensitivity.
-
Low VIX = less Vega effect, cheaper premiums.
Where to track it:
-
Dhan Option trading App, Sensibull, Opstra, TradingView etc.
Vega Trading Strategies:
Case Study 1: Profiting from Rising Vega – Earnings Straddle on ABC stock
-
Stock: ABC
-
Pre-Earnings IV: 20%
-
ATM Call & Put Prices: ₹120 & ₹100
-
Vega: 0.18
Trade Setup:
-
Buy ATM Call & Put (Straddle) – High Vega benefits from IV increase.
Post-Earnings Outcome:
-
IV increases to 30% – Option premiums rise.
-
Straddle price jumps from ₹220 to ₹300.
-
Profit: ₹80 per lot.
Tip: Buying high Vega before earnings works if IV increases as expected.
Case Study 2: Losing Money Due to Vega Crush – Bank Nifty Event Trade
-
Index: Bank Nifty
-
IV Before RBI Decision: 35%
-
Bought ATM Call at ₹500 (High Vega of 0.25)
-
IV Drops to 28% After Decision
Result:
-
Vega decreases → Option price falls to ₹400.
-
Loss: ₹100 per lot due to Vega crush.
What Went Wrong?
-
Entered trade when Vega was already high.
-
IV drop reduced the option’s value even when the price moved favorably.
Tip: Avoid buying options with high Vega unless you expect IV to continue rising.
How to Hedge Against Vega Risk:
1. Vega-Neutral Strategies
-
Iron Condor & Iron Butterfly – Balance long and short Vega exposure.
-
Calendar Spreads – Use different expiries to hedge Vega risk.
2. Avoiding Overpaying for Vega
-
Check India VIX before entering high Vega trades.
-
Compare current IV with historical IV ranges.
-
Use options with moderate Vega if uncertain about IV trends.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Option Greeks Comparison Table:
Greek |
Sensitivity To |
Best Used For |
Risk Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
Delta |
Underlying price movement |
Directional strategies |
Market bias |
Vega |
Implied volatility |
Volatility strategies |
Event risk |
Theta |
Time decay |
Income strategies |
Expiry risk |
Gamma |
Delta changes |
Hedging + ATM scalping |
Volatility shocks |
Final Thought: Why Understanding Vega is Crucial for Option Traders
-
Vega helps traders predict how option prices react to IV changes.
-
Proper Vega analysis prevents overpaying for options.
-
Using Vega-based strategies can significantly improve profitability.
- Vega is crucial for predicting option price movements.
- Understanding IV can prevent costly trading mistakes.
Do’s and Don’ts When Trading Vega
✅ Do’s:
✔ Track IV trends before entering a trade.
✔ Use Vega-heavy strategies (like straddles) when expecting IV rise.
✔ Hedge Vega risk using spreads.
❌ Don’ts:
✘ Don’t buy options with high Vega right before earnings unless you expect continued IV rise.
✘ Avoid selling options with low Vega before major events (IV can spike).
✘ Don’t ignore India VIX trends when analyzing Vega.
To succeed in options trading, always analyze Vega along with Delta, Gamma, and Theta before making a trade!. Keep an eye on India VIX, use Vega wisely with ATM strikes, and combine it with other Greeks for stronger trades.
If you are looking for the best stockbroker for option trading I would recommend you to checkout this broker, or you can directly use the below link to open the account free of cost.
Quick Quiz – Test Your Vega Knowledge
-
Which option has the highest Vega?
-
A) Deep ITM
-
B) ATM
-
C) Deep OTM
-
-
What happens when IV crashes after an event?
-
A) Option premiums go up
-
B) Vega increases
-
C) Option premiums drop
-
-
What does India VIX measure?
-
A) Interest Rate
-
B) Volume
-
C) Expected Market Volatility
-
Disclaimer:
The information provided in this article is for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as investment advice or a recommendation to buy or sell any securities or derivatives. Options trading involves significant risk and is not suitable for all investors.
While efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, the author and platform do not guarantee completeness or reliability of any content, graphs, or examples provided. Past performance is not indicative of future results.
Please consult with a SEBI-registered financial advisor before making any investment decisions. The author or the platform shall not be held responsible for any losses or damages arising directly or indirectly from the use of the information provided.




